Book Discription
Revenue Management: Hard-Core Tactics for Market Domination
Introduction
In Revenue Management, Robert G. Cross provides a fresh perspective on business growth. Unlike traditional cost-cutting methods that often lead to short-term profits and unhappy shareholders, Cross advocates for a different approach: focusing on generating revenue instead of reducing expenses. This groundbreaking strategy challenges conventional marketing wisdom and offers a roadmap for sustainable growth.
The Problem with Cost-Cutting
Over the years, many companies have become fixated on cost-cutting as a means to improve their financial performance. While reducing expenses can certainly have its benefits, it’s not the ultimate solution for long-term success. In fact, this singular focus on cost control has caused businesses to overlook the importance of revenue generation.
The Solution: Revenue Management
Revenue Management, also known as RM, is a comprehensive approach that aims to optimize an organization’s revenue streams. It combines mindset shifts, advanced technology, and innovative marketing tactics to drive profitability. Drawing from his extensive experience working with major corporations, Cross shares real-life examples of how companies across various industries have successfully implemented RM strategies.
Key Concepts in Revenue Management
1. Market-Based Pricing
Contrary to popular belief, setting prices based on costs alone is not always the most effective strategy. Instead, businesses should adopt market-based pricing, which involves determining the value customers place on a product or service and adjusting prices accordingly. This approach allows companies to capture maximum value from their offerings without solely relying on cost reduction.
Be the first to know, sign up here and stay up to date with our latest revenue management news, updates and special offers
2. Targeting High-Value Customers
Not all customers are created equal. Some bring more value to a business than others through their purchasing habits, loyalty, or willingness to pay premium prices. In Revenue Management, Cross emphasizes the importance of identifying and prioritizing these high-value customers. By understanding their needs and preferences, companies can tailor their offerings and allocate resources more effectively.
3. Product Life Cycle Management
Every product goes through a life cycle, starting from its introduction to the market until its eventual decline. Revenue Management highlights the significance of comprehending this life cycle and making dynamic decisions based on its different stages. For example, during the growth phase, companies may choose to invest more in marketing and production to capitalize on increasing demand.
Benefits of Revenue Management
Implementing effective Revenue Management practices can yield several advantages for businesses:
- Increased Revenue: By optimizing pricing strategies and targeting high-value customers, companies can generate more sales and revenue without necessarily expanding their product offerings.
- Improved Operational Efficiency: Through the use of technology and data analysis, businesses can better understand customer behavior, anticipate demand fluctuations, and streamline their operations accordingly.
- Market Expansion Opportunities: Revenue Management encourages organizations to explore new markets and customer segments that align with their value proposition. This approach opens doors for growth beyond existing boundaries.
- Enhanced Customer Satisfaction: By delivering products and services that precisely meet customer needs at competitive prices, companies can foster stronger relationships and enhance overall satisfaction levels.
Conclusion
In today’s competitive business landscape, focusing solely on cost-cutting is no longer sufficient for sustainable growth. Revenue Management offers a compelling alternative that prioritizes revenue generation while maintaining operational efficiency. Through this book, Robert G. Cross provides invaluable insights and strategies for any company looking to thrive in their respective markets.
Book Information
Print Length

288 Pages
Language

English
Publisher

Currency
Publication Date

December 29, 1997
Dimensions

5.51 x 0.77 x 8.24 inches
ISBN-10
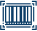
0767900332
ISBN-13

978-0767900331